
Lumbago is the clinical term for lower back pain. Back pain is not a disorder. It’s a symptom of several clinical disorders, and it is easy to manage back pain than you think.
Back pain usually occurs as a result of problems with the lower back, such as:
- Muscles
- Ligaments
- Nerves
- The bones of the spine, known as vertebral bodies or vertebrae.
Back pain may also be caused by problems with the kidney and other nearby organs.
Back Pain Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis & Treatment:
A study by the American Association of Neurological Surgeons shows that at least 75% of Americans may experience back pain within their lifetime. The report also indicates that up to 50% of these patients will experience at least two episodes per year.
In most conditions, the pain usually resolves without surgery. If you are experiencing back pains, you should consult your doctor.
How is Back Pain Treated?
Most people may not need intense treatment for back pain. Sometimes, over-the-counter medications may be just enough to manage back pain.
In extreme situations, stronger treatments may be required, but you should do under a doctor’s supervision.
Medication to manage back pain:
Doctors usually manage back pain by prescribing NSAIDs, such as:
- Naproxen
- Ibuprofen
Analgesics or pain reliever such as Tylenol, are also administered, although they lack anti-inflammatory effects.
Patients should take great care with medications such as ibuprofen if they have underlying conditions such as stomach ulcers or kidney problems.
As much as you can, avoid taking more than the prescribed dose, as you may suffer some side effects if you take over or below the recommended dose.
Other forms of medication used to manage back pain include:
Ointments & topical medications to manage back pain:
Topical medications are great for lower back pain treatment at home. These medications contain ingredients such as ibuprofen and lidocaine, both more potent than a placebo when it comes to back pain management.
Opioids:
They are effective medications prescribed for lower back pain treatment at home. They are very effective in the management of severe back pain. These medications, like oxycodone, hydrocodone, and acetaminophen, exert their effects on cells of the brain. Also, the body to minimize the pain.
Users should exercise caution during opioid usage, as there is a high risk of addiction.
Muscle relaxants:
Muscle relaxants help to manage back pain. They mostly used when muscle spasms accompany the pain. These medications exert their effect on the central nervous system.
Antidepressants:
Sometimes, antidepressants may be used off-label to manage back pain.
If the pain is of high intensity, the doctor may prescribe tricyclic antidepressants, mostly amitriptyline. Amitriptyline is helpful in the management of pains related to nerves.
Steroid injections:
Sometimes, your doctor might use corticosteroid injections to manage back pain. But then, relief from steroid injections doesn’t last for long. They wear off usually within three months.
Surgery:
Surgery is usually the last treatment of choice but not required in most cases. Doctors recommend surgery only when back pain caused by structural defects – defects that have failed to respond to treatment with therapy and medicines.
These include:
- Very severe pain
- Compression of nerve fibers that causes weakening of the muscles
Spinal fusion is a form of surgery characterized by the fusion of a painful vertebra into one single bone. It blocks painful spinal motion.
Sometimes, the doctor might manage back pain through partial removal and replacement of vertebrae and disks. Mostly, this is done to relieve back pain caused by bone diseases.
Alternative therapies for the management of back pain:
Alternative treatments to manage back pain include:
- Acupuncture
- Massage
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy
- Relaxation techniques
- Chiropractic adjustments
You must get your doctor’s consent before partaking in any alternative or complementary therapies.
LOWER BACK PAIN TREATMENT AT HOME
There are many remedies that you can use to manage back pain at home. If you are confused about these, you may talk to your doctor.
Heat & ice therapy:
Ice packs may minimize inflammation and ease discomfort in the case of acute back pain. You mustn’t apply the ice to your skin directly. Instead, fold it in a thin towel or gauze to prevent skin damage.
You may also relieve the pain using warm compresses. You may try alternating between cold and heat.
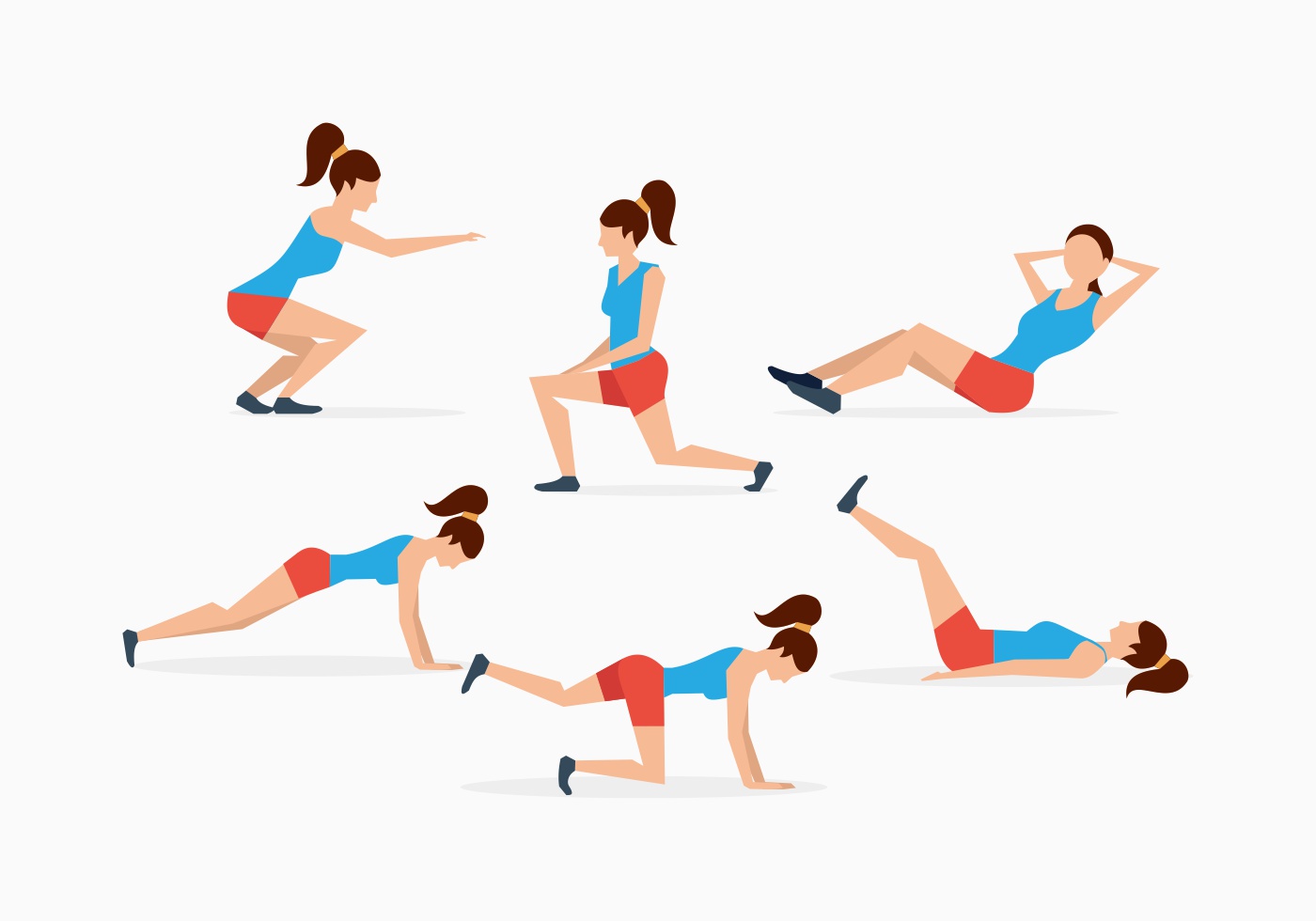
Back pain exercises:
Exercises help to strengthen and improve the back muscles as well as the muscles of the abdomen (also known as core muscles). Back pain exercises are an option that should be given serious consideration.
Treatment of back pain with exercises include:
- Improvement of posture
- Stretch of the muscle to enhance flexibility
- Strengthening abdominal muscles
- Using the right lifting techniques
These exercises may have taught by a physical therapist.
Essential oils:
According to research, ointments, or essential oils containing capsaicin may help reduce back pain.
Capsaicin gives the unique spicy taste of pepper. These ingredients desensitize the nerve fibers, and in the area of the body that impacted and decreases the intensity of the pain you feel.
Salt bath:
Bathing in hot water is beneficial for aching muscles. However, while you are immersed in the water, you can boost its therapeutic potential through the addition of Epsom salt. The human body can absorb the minerals, and they relieve the muscle aches.
Back pain home remedies are highly effective in many cases.
WHAT CAUSES BACK PAIN?
The primary causes of back pain are anatomical defects and strain.
Strain:
Back pain often results from muscle strain. Strain usually occurs when a person lifts heavy objects in the wrong way. Awkward movements occurring suddenly also contribute to strains.
Over-activity may also contribute to strain. An instance is a painful and stiff sensation that occurs after doing some yard work for a couple of hours, or after playing.
Anatomical defects:
Vertebrae are bones that have an interlocking structure. They are stacked on top of each other, resulting in the formation of the spine. Disks are those parts of a tissue that acts as cushions for the spaces between each vertebra. In most cases, back pain causes due to disk injuries.
Sometimes, the disks may herniate, rupture, or bulge. Nerve fibers may be compressed if any of these happens.
Herniated disks cause severe pain. The sciatic nerve gets irritated when a bulging disc compresses the nerve that travels from your back to your leg. Symptoms of sciatica include:
- Numbness
- Tingling
- Pain
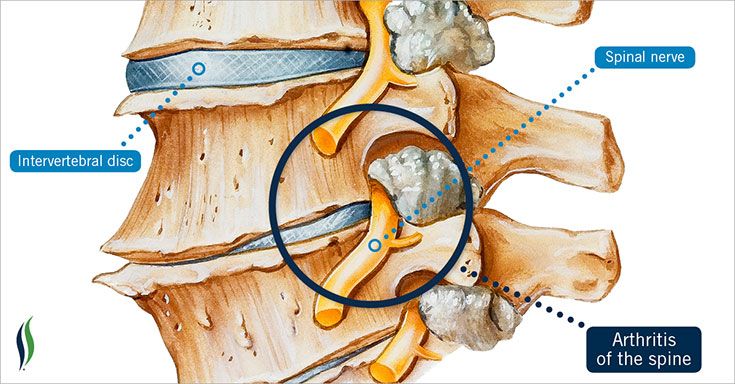
Arthritis:
Spinal osteoarthritis is another major cause of back pain. Arthritis caused by the deterioration of joint cartilage in the lower back.
Subsequently, this condition may result in spinal stenosis or narrowing of the spinal column.
Osteoporosis:
Osteoporosis is a condition that is characterized by thinning of the bone or loss of bone density. That can result in a vertebral fracture. These fractures cause intense pain and termed compression fractures.
Other factors that contribute to back pain:
Several other factors cause back pain, but they are rare, mostly. You must consult your doctor if you are experiencing severe back pain that refuses to go away in spite of treatment.
After ruling out the major causes of back pain, your doctor will run a few tests to check if you have any rare underlying disorder. Such include:
- Degenerative spondylolisthesis
- Cauda equina syndrome (or loss of neural function at the lower level of the spinal cord).
- Infection of the spinal cord by bacteria or fungi, including E. coli, Staphylococcus, or tuberculosis.
- Nonmalignant tumor or cancer in the spine
- Kidney stones or kidney infection
SYMPTOMS OF BACK PAIN
Back pain is associated with many symptoms. These include:
- A dull and aching sensation in the lower part of the back
- A shooting or stabbing pain that radiates through the leg to the foot.
- Being unable to stand straight without pain
- Inability to flex the back or a reduced range of motion
Symptoms of back pain do not last for long, especially if they are due to misuse of strain. The duration may be from a few days to some weeks.
A person has chronic back pain when he or she experiences the symptoms persist for more than three months.
Some symptoms may indicate a severe problem:
You must consult your doctor if your pain does not resolve within two weeks. Sometimes, back pain may indicate a serious underlying condition.
The following symptoms of back pain may indicate a severe underlying medical disorder:
- Inability to control the bladder or bowel
- Tingling, weakness, or numbness in either or both legs
- The back pain follows a trauma, such as a blow to the back of a fall.
- Intense and constant pain that worsens at night
- Weight loss whose origin cannot be explained
- Fever
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, do not hesitate to inform your doctor.
DIAGNOSING BACK PAIN
A physical examination is an essential requirement for diagnosing back pain. During the examination, your doctor will test the following features:
- Your ability to walk and stand
- Reflexes
- Range of motion of your spine
- Leg strength
If there’s a serious underlying condition, your doctor will order more tests, such as:
- Urine and blood tests to check for underlying conditions
- Spinal X-rays to bone alignment
- Magnetic resonance imaging or computed tomography scans to assess your muscles, discs, nerves, blood vessels, and ligaments
- Bone scan to check for abnormalities in bone tissue
- Electromyography for nerve conduction tests
TIPS TO MANAGE BACK PAIN:
Sometimes, it may be pretty hard to determine the leading cause of back pain, but there are a few tips to alleviate the pain or prevent it from worsening. Management of back pain is all about reducing strain, relieving pressure, muscle strengthening, and protecting one’s spine. A few lifestyle modifications can help you keep your back healthy and pain-free for a long time.
-
Put a pillow beneath your knees when sleeping
When you sleep on your back, you put a lot of pressure on your spine. Slight elevation of the legs relieves this pressure. You can reduce the pressure by placing a pillow under your knees.
-
Core strength training
We all know the positive benefits of exercise. A strength training routine that focuses on core muscles can minimize one’s risk of back-related injuries such as muscle spasms and strains. As much as you can, incorporate abdominal strengthening exercises and back strengthening exercises into your workout, perhaps twice weekly. It will help you to build a more flexible and stronger back.
-
Increase your intake of calcium & vitamin D
Strong bones help to prevent osteoporosis. Osteoporosis is a significant cause of back pain, especially in one’s later life. You can maintain the strength of your bones by taking in a lot of vitamin D and calcium. Calcium is naturally present in food such as:
- Yogurt
- Milk
- Leafy greens
- Milk
- Vitamin supplements
Vitamin D is present in:
- Beef liver
- Egg yolks
- Fatty fish
- Cheese
You must seek your doctor’s consent before taking supplements to manage back pain.
-
Consider your shoes
Always put on low-heeled and comfortable shoes. They are very effective at preventing back pain. Low-heeled shoes reduce the strain on the back when a person stands. You are better off wearing shoes whose heels are less than an inch high.
-
Maintain a straight posture
A straight posture gives you a good look. But not only that, It also protects your spine and keeps them functioning at optimum conditions. Bad posture stresses and strains your back and may alter the architecture of your spine. As much as you can, avoid slouching, bending sideways, or rounding the shoulders when standing.
-
Avoid slumping over your desk
Maintain a good posture when sitting on an office chair. You must maintain a good posture when sitting. Good back support is also necessary. Get a good chair that supports your lower back firmly and ensure that your knees are slightly higher than your hips when sitting.
People also search for:
- How to manage back pain in 2020?
- How to reduce back pain fast in 2020?
ARTICLE SOURCES:
- Mayo Clinic Staff. (2016, April 22). Prevent back pain with good posture
mayoclinic.org/healthy-living/adult-health/multimedia/back-pain/sls-20076817 - Preventing back pain at work and at home. (2012, March)
orthoinfo.aaos.org/topic.cfm?topic=A00175 - Vitamin D: Fact sheet for health professionals. (2016, February 11)
ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/VitaminD-HealthProfessional/ - Back pain. (2018).
medlineplus.gov/backpain.html - Chang A, et al. (2018). Capsaicin.
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459168/ - Low back pain. (2013).
orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/diseases–conditions/low-back-pain - Mayo Clinic Staff. (2018). Back pain.
mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/back-pain/symptoms-causes/syc-20369906 - Low back pain fact sheet. (2018).
ninds.nih.gov/Disorders/Patient-Caregiver-Education/Fact-Sheets/Low-Back-Pain-Fact-Sheet - The best meds for back pain. (2018).
health.harvard.edu/pain/the-best-meds-for-back-pain


More Stories
Right Side Back Pain Symptoms, Causes and Treatments
What Tips for avoiding and treating mid back pain?
Can Spine Arthritis Cause Back Pain?